Episode 570
January 4, 2020
How do you connect to the Internet?
My iPhone connects to T-Mobile’s cell towers.
When i am home my iPhone, iPads and computer connect to my WiFi.
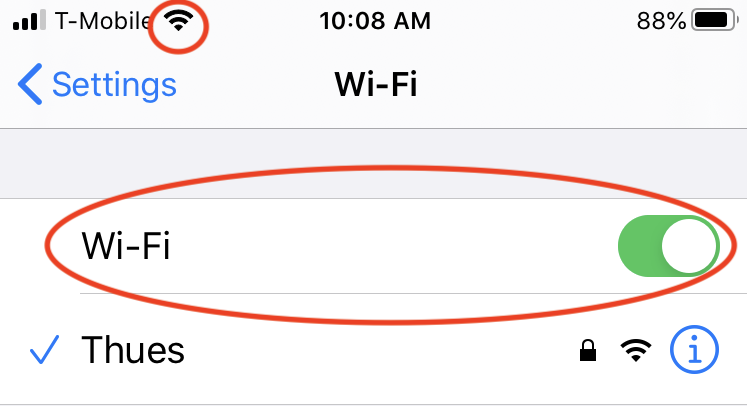
When connected to WiFi the iPhone does not use the T-Mobile cell connection.  WiFi has priority on iPhones and iPads.
WiFi has priority on iPhones and iPads.
The other day i was in town with three bars on my cellular connection, yet i could not get the Internet. i noticed that i was also connected to a regional ATT WiMax terrestrial WiFi hot spot. Since i no longer subscribe to ATT the connection did not provide me with the Internet. i turned my WiFi off on the iPhone and suddenly got Internet via the T-Mobile LTE cell signal.
WiFi usurped the cell signal.
A similar thing happened while visiting my sister. Her cable company line broke under the weight of the snow. Her router continued to broadcast, but did not have the Internet. As long as i stayed connected to her router’s WiFi i had no Internet connection on my iPhone. As soon as i turned off WiFi the T-Mobile cell signal took over and i was able to surf and receive my email.
Some people pay for a cellular hot spot. This device converts a local cell signal to WiFi which can be joined by up to 10 people. The people joining the hot spot must be fairly close to the device (20 meters maximum). These cellular hot spot devices can cost up to $500 and might add a line to your cellular service monthly fee. They also are subject to data caps and throttling by your service provider. The speeds are dictated by the local cellular connection. If you have a data cap on your cell service you do not want to use a hot spot to stream video.
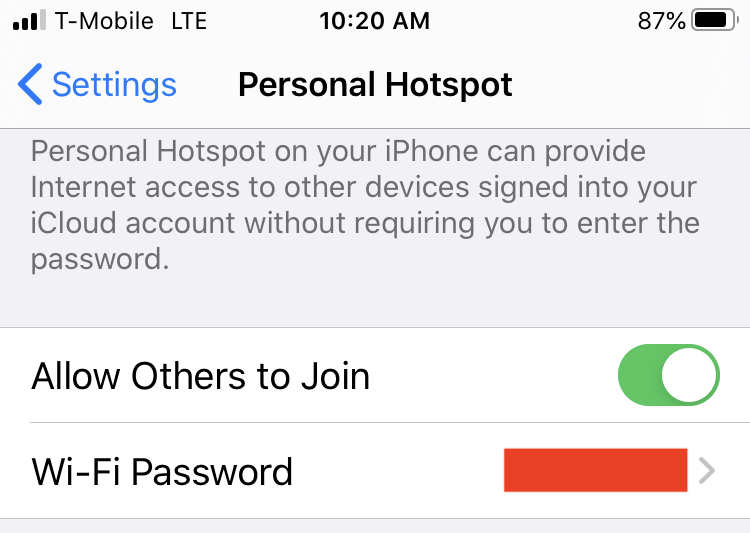
Another way to create a WiFi hotspot is to use your cell phone. On the iPhone go to Settings > Personal Hotspot > turn on “Allow Others to Join”. A WiFi password will be provided or you can change it to something you like. Others can connect to your Personal Hotspot via WiFi, Bluetooth or with a USB cable. Data consumed from the Hotspot is subject to your cell phones data plan. Speeds are subject to the local cell connection.
Terrestrial WiFi is available in many metropolitan areas, but may require a service plan (such as the ATT hotspot mentioned above).
Public places might make WiFi available for free. Airports, hotels and cafés are examples. Be cautious connected to public WiFi that does not require a password (open WiFi), such as at airports. Open WiFi can be hacked by others. Your data can be collected in transit.
There are various ways to obtain Internet in your home. WiMax terrestrial WiFi, satellite, telephone dialup, fiberoptic and cable are the most common. Additionally, services like SpaceX’s Starlink satellite constellation will provide WiFi all over the world from low orbit satellite arrays.
WiMax is WiFi broadcasted to an antenna on your house. This WiFi is transferred directly to your router and then distributed as a Local Area Network (LAN) via ethernet cables or WiFi in your house. These services are typically slow and expensive.
Satellite Internet is received by an antenna on your house, transferred to a modem, then to your router for WiFi or ethernet cable distribution. It is also slow and expensive.
Telephone dialup is rare nowadays. It has been abandoned because of its extremely slow speeds. Streaming video is not possible with dialup.
Cable and fiberoptic are the most typical home Internet services. They can deliver data, telephone and TV. The costs range from $50 to $100 per month for data only. Speeds are typically 100 Mbps or faster.
Starlink satellite constellation will reportedly provide fast speeds and low cost anywhere in the world. This may very well eliminate the need for cellular services.
The trick of connecting to the Internet is to know where it is coming from and to arrange for the connection that you need. Subscribe to the connection you want and configure your device to connect to the best service where you are.